Inulin Nutrition Facts
| Nutrition Facts | |
|---|---|
| For a Serving Size of 1 scoop (5g) | |
| Calories 20 | Calories from Fat 0 (0%) |
| % Daily Value * | |
| Total Fat 0g | - |
| Sodium 0mg | 0% |
| Carbohydrates 5g | - |
| Net carbs 0g | - |
| Fiber 5g | 20% |
| Protein 0g | |
| Vitamins and minerals | |
| Fatty acids | |
| Amino acids | |
| * The Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet, so your values may change depending on your calorie needs. |
What are the benefits of inulin?
As someone interested in health and nutrition, I often come across interesting ingredients that promise various benefits. Recently, I've been hearing more about inulin, a dietary fiber that is found naturally in certain foods and added to others. With weight loss being a common goal for many people, I wanted to find out - can inulin help with weight loss?
After doing thorough research from reputable sources, it seems the answer is a cautious yes. While bulk inulin is not a magic bullet for weight loss, it does appear to provide some potential benefits that can aid in a healthy weight loss regimen when combined with a calorie-controlled diet and exercise. Let's take a closer look at inulin, where it comes from, how it works in the body, and the research around its effects on appetite, weight loss, and overall health.
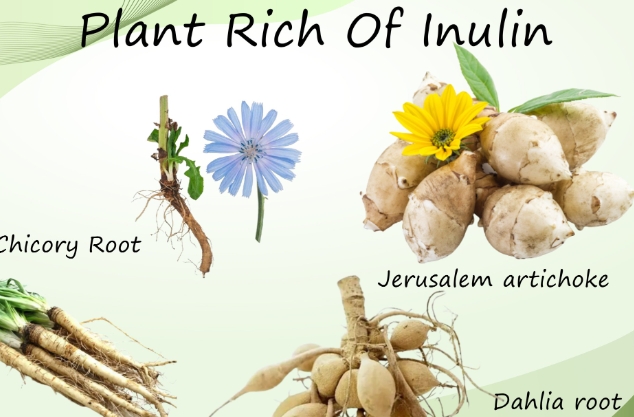
What is Inulin?
Inulin is a type of soluble dietary fiber found naturally in a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Some foods particularly high in inulin include chicory root, onions, garlic, asparagus, bananas, and wheat. Inulin is actually a term for a collection of carbohydrate fibers known as fructans. The fibers are made up of fructose molecules chained together.
Inulin is considered a form of soluble fiber because it dissolves in water to form a gel-like material. Unlike other fibers that lend bulk, inulin acts as a prebiotic once in the intestines. Prebiotics are compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. So while inulin passes through the small intestine undigested, once it reaches the colon it becomes food for probiotics or “good” bacteria like bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
This prebiotic effect is thought to be one reason wholesale inulin may provide health bonuses beyond basic fiber. Some supplements and foods are now enriched with inulin powder from chicory roots to boost the prebiotic fiber content.

How Does Inulin Aid Weight Loss?
Preliminary research indicates inulin may help support weight loss efforts in a few key ways:
Suppressing Appetite
Several studies on both animals and humans have found that inulin consumption leads to increased satiety or feelings of fullness compared to control groups. One study had participants consume 10 grams of inulin from chicory per day. The inulin group reported higher subjective ratings of satiety during the test meals compared to placebo.
Researchers believe improved satiety from inulin comes from multiple effects. The prebiotic fiber appears to help slow down digestion, which prolongs feelings of fullness. As it ferments in the colon, inulin also promotes the release of satiety hormones like peptide YY and glucagon-like peptide-1 from intestinal cells.
By regulating appetite-controlling hormones and digestion, inulin may help curb overeating and reduce total calorie intake over time, which aids weight loss.
Altering Fat Storage
Some emerging research suggests inulin may help alter where and how the body stores fat. Animal studies have found supplementing with inulin led to less intra-abdominal fat storage compared to control groups.
One reason may be that inulin's effect on gut flora improves insulin sensitivity and related fat-regulating hormones. The prebiotic fiber has also been shown to suppress certain genes involved in fat storage like LPL and FAS. This regulation of fat-storing mechanisms could make it easier to shed unwanted pounds.
Boosting Metabolism
A few promising studies hint that bulk inulin powder may give metabolism a slight boost, which could increase calorie burn.
In one trial, healthy adults who consumed 21 grams of inulin per day had increased post-meal energy expenditure compared to those given maltodextrin fiber. Another longer study found overweight women who took inulin for 3 months experienced significantly increased oxidation or fat burning compared to placebo.
While more research is needed, the prebiotic activity of inulin apparently helps support a diverse microbiome. In turn, this beneficial gut flora may aid energy regulation and weight control.
Supporting Fat Loss with Diet and Exercise
Currently, there isn't strong evidence that inulin supplementation alone will lead to significant weight loss. However, when combined with traditional weight loss strategies like portion control, exercise, and a reduced-calorie diet, inulin may provide an added edge for losing fat.
By blunting appetite and cravings, altering fat storage patterns, and slightly revving metabolism, inulin works through several mechanisms that complement lifestyle changes for losing weight. For example, one study found that women following a low-calorie diet lost 3 pounds more over 3 months when also taking inulin compared to just dieting alone.
Researchers believe a daily inulin intake between 5-20 grams offers optimal benefits for appetite and weight control. Amounts up to 30 grams are considered safe for most healthy adults. Personally, I like to get in 10-15 grams per day from foods like chicory root veggies, garlic, onions, and chia seeds to support my weight loss regimen.
What Other Health Benefits Does Inulin Offer?
In addition to potential weight loss bonuses, inulin touts several other evidence-based health benefits:
Heart health – Inulin may lower heart disease risk by reducing blood triglycerides, cholesterol, and blood pressure. The prebiotic effect also limits inflammation tied to heart disease.
Blood sugar regulation – By enhancing insulin sensitivity and secretion, organic inulin powder bulk helps control blood sugar spikes after eating. Long-term use may lower diabetes risk.
Immunity – Through nourishing good gut flora, inulin boosts immunity and helps prevent growth of harmful bacteria in the intestines.
Mineral absorption – Inulin has been shown to increase the uptake of calcium and possibly magnesium, aiding bone density and strength.
Gut health – As a prebiotic, inulin feeds probiotics and maintains the optimal balance of microflora for digestive health. It may ease certain conditions like constipation, IBS, and leaky gut.
Cancer prevention – Some research indicates inulin may suppress early formation of colon cancer tumors. More data is still needed.
The prebiotic activities of inulin offer clear synergistic benefits when combined with probiotic foods and supplements. I make sure to take both prebiotics like inulin and probiotics daily to maintain microbiome balance.
Are There Any Side Effects of Inulin?
Inulin is generally well tolerated, especially when ramped up gradually in the diet. However, some people may experience unpleasant GI side effects if too much is consumed too quickly. The most common side effects are:
Gas and bloating – Excess gas is caused by the rapid fermentation of inulin in the colon. This usually subsides with consistent intake.
Diarrhea – Some people's bowels are sensitive to the osmotic effect of soluble fibers like inulin, which pulls more water into the colon. Start with small amounts.
Abdominal pain – In some sensitive individuals, inulin may cause temporary cramps or discomfort. This typically improves with slower introduction.
To help minimize adverse effects, it's best to transition up to higher inulin intakes slowly over several weeks. Most people can ultimately tolerate up to 30 grams per day, spread throughout meals. Also, be sure to drink adequate water daily. Inulin requires sufficient fluid in the colon to ferment properly.
Those with digestive disorders like IBS may need to be especially cautious with higher doses of inulin at first. As always, it’s wise to consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially with any underlying medical conditions.

Top Whole Food Sources of Inulin
Given the promising weight loss and health benefits of bulk organic inulin powder, it makes sense to consume more of this prebiotic fiber through whole foods. Here are some of the best dietary sources of inulin:
Chicory root – The highest natural source, with over 20% inulin content. Eat the root or leaves as a vegetable. Also used to make chicory coffee.
Jerusalem artichoke – Around 10-15% inulin; eat the root raw or cooked like potatoes.
Garlic – One clove contains around 1 gram inulin.
Onion – A good source with 1-2 grams per medium onion.
Asparagus – 5 grams inulin in 1 cup.
Banana – Contains approx. 2 grams per fruit. Under-ripe bananas have more.
Chia seeds – 10 grams per ounce; stir into smoothies, oatmeal, yogurt.
Dandelion Greens – 5 grams per 100 grams; use raw in salads or sautéed.
Konjac Root – Used to make shirataki noodle products; high inulin content.
As you can see, it’s easy to incorporate inulin-rich foods into meals and snacks to take advantage of this fiber’s weight loss benefits. An inulin powder supplement from chicory root is also a convenient way to increase daily intake.
The Bottom Line on Inulin for Weight Loss
When examining the latest research, it appears the prebiotic fiber inulin can promote modest fat loss when combined with a healthy diet and active lifestyle in several ways:
Inulin increases feelings of fullness and helps curb calorie intake and cravings.
It may alter how and where fat is stored in the body.
Early studies suggest inulin could slightly boost metabolism and fat burning.
Doses of 5-30 grams per day enhance weight loss from calorie-controlled diets and exercise.
While not a panacea, inulin is an easy addition to any regimen to promote fat burning and lean body composition. As a bonus, it provides other benefits for digestion, immunity, blood sugar control, and heart health. Include inulin in both foods and supplements as part of an overall healthy lifestyle for lasting weight management.
If you have any inquiries or would like more information about inulin powder, feel free to contact us at info@scigroundbio.com.
References:
Cani PD, Joly E, Horsmans Y, Delzenne NM. Oligofructose promotes satiety in healthy human: a pilot study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006 May;60(5):567-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602394. Epub 2005 Nov 9. PMID: 16288275.
Parnell JA, Reimer RA. Weight loss during oligofructose supplementation is associated with decreased ghrelin and increased peptide YY in overweight and obese adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009 Jun;89(6):1751-9. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27465. Epub 2009 Apr 29. PMID: 19403639.
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Maton N, Delzenne NM. Oligofructose promotes satiety in rats fed a high-fat diet: involvement of glucagon-like Peptide-1. Obes Res. 2005 Jun;13(6):1000-7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2005.117. PMID: 15976141.
Chambers ES, Viardot A, Psichas A, et al. Effects of targeted delivery of propionate to the human colon on appetite regulation, body weight maintenance and adiposity in overweight adults. Gut. 2015 Nov;64(11):1744-54. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307913. Epub 2015 Mar 30. PMID: 25825000.
Abrams SA, Griffin IJ, Hawthorne KM, Liang L, Gunn SK, Darlington G, Ellis KJ. A combination of prebiotic short- and long-chain inulin-type fructans enhances calcium absorption and bone mineralization in young adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 Aug;82(2):471-6. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/82.2.471. PMID: 16087995.
FDA. FDA provides data on inulin and fiber content of foods. https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-provides-data-inulin-and-fiber-content-foods
ABOUT AUTHOR

Celine Xu is a botanist with over 15 years of experience researching and developing plant extracts for nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. She leads an R&D team focused on identification, cultivation and extraction of medicinal plants. Celine Xu earned a Ph.D. in Plant Biology has authored numerous articles in peer-reviewed journals about the health benefits of specific phytochemicals. She frequently speaks at industry conferences about new developments in plant extract research. Celine Xu is dedicated to advancing the scientific understanding of how targeted plant compounds can be used to improve human health.
Related Industry Knowledge
- What are the benefits of Mallow Extract?
- Is tannic acid in all tea bags?
- What is the most effective form of quercetin?
- What are the health benefits of inositol powder?
- Is it safe to eat cinnamon powder everyday?
- What is capsaicin powder used for?
- Soybean Seed Extract: What You Need to Know
- Butcher's Broom Extract: A Natural Remedy for Circulatory Health
- When to drink bcaas
- How Does Capsaicin Work?







