Quercetin vs COQ10
Quercetin and CoQ10 (coenzyme Q10) are two of the most famous cell reinforcement supplements taken today. The two mixtures give huge cell reinforcement and calming impacts that can help wellbeing and battle sickness. However, what precisely are quercetin and CoQ10? How would they function and how would they think about? This complete article audits what quercetin and CoQ10 are, their instruments and advantages, whether you can take them together, and which might be better for your requirements.

What Is Quercetin?
Quercetin is a strong cell reinforcement flavonoid tracked down normally in many organic products, vegetables, teas and grains. Its compound construction is 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)- 3,5,7-trihydroxychromen-4-one. Probably the best food wellsprings of quercetin include:
Onions
Apples
Broccoli
Berries
Green tea
Red wine
Capers
As a flavonoid antioxidant, quercetin helps scavenge damaging free radicals and reduces oxidative stress. It also has strong anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting inflammatory pathways like NF-kB. Some benefits of taking quercetin supplements may include:
Reduces inflammation
Fights allergies and histamine
May lower blood pressure
Helps control blood sugar
Has anticancer properties
Protects cardiovascular health
Boosts exercise endurance
Improves immunity
Reduces risk of degenerative neurological disease
Overall, bulk quercetin powder is a powerful flavonoid antioxidant with a wide range of potential health benefits. The typical dosage of quercetin supplements ranges from 200 mg to 500 mg per day.
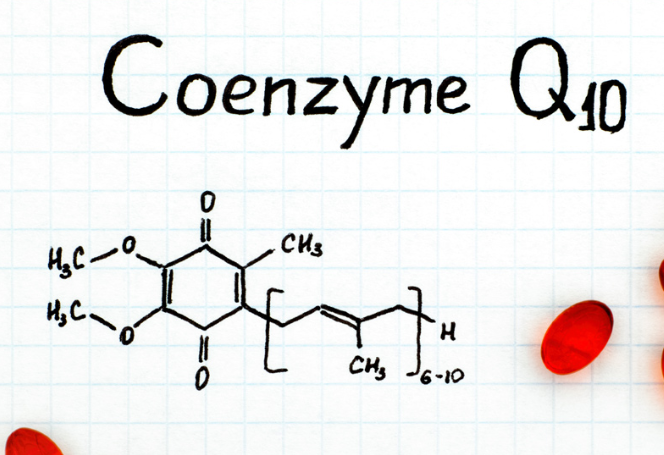
What Is Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10, otherwise called CoQ10 or ubiquinone, is another critical cell reinforcement compound delivered normally inside the body. It is a vital mitochondrial component that aids in the conversion of food into cellular energy.
Powerful antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress
Major player in the electron transport chain for ATP energy production
Helps regenerate other antioxidants like vitamin E
Required for proper mitochondrial function
Coenzyme Q10 production in the body decreases with age. Thus, CoQ10 oral supplements have gained popularity to help maintain optimal levels in the body. Benefits of CoQ10 supplementation include:
Improves heart health and function
May help lower blood pressure
Helps treat heart failure and prevents damage from statin drugs
Improves exercise performance and reduces fatigue
Slows decline in Parkinson’s disease
Protects against migraines and headaches
May improve male fertility
Boosts immune function
Anti-aging benefits for skin and cells
The standard daily dosage for CoQ10 supplements ranges from 100 mg to 300 mg per day.
Is Quercetin the Same as CoQ10?
No, quercetin and CoQ10 are completely different compounds. Quercetin is a flavonoid antioxidant found in plants while CoQ10 is an antioxidant synthesized within the human body. They provide overlapping benefits but have distinct mechanisms of action:
Quercetin is a flavonoid antioxidant while CoQ10 is a mitochondrial antioxidant.
Quercetin scavenges free radicals while CoQ10 regenerates other antioxidants like vitamin E.
Quercetin reduces inflammation through inflammatory pathways while CoQ10 supports energy production.
Bulk Quercetin is plant-derived while CoQ10 is produced within the body.
So while both act as antioxidants, quercetin and CoQ10 differ in their structures, sources, and specific mechanisms of action within the body.
Dietary Quercetin and Coenzyme Q10
Since CoQ10 is produced within the body, intake from food sources is limited. Some dietary sources of CoQ10 include:
Organ meats like liver, kidney and heart
Fish like trout, herring and mackerel
Whole grains
Soybean and canola oil
Nuts like peanuts and pistachios
Meanwhile, quercetin is found abundantly in plant-based foods like:
Red onions
Green tea
Apples (Buy Apple Extract Powder)
Berries
Cruciferous veggies like broccoli (Buy Broccoli Extract Powder) and kale
Tomatoes
Asparagus
Capers
For those looking to maximize quercetin and CoQ10 intake naturally, eat a balanced diet with plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, lean meats, fish, nuts, seeds and whole grains.
Effects of Quercetin Supplementation
Research indicates supplemented quercetin offers significant health benefits:
May improve exercise endurance by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells.
Lowers markers of inflammation like TNF-alpha and IL-6 according to meta-analyses of clinical studies.
Reduces intestinal inflammation, stool frequency and other symptoms in inflammatory bowel disease patients.
May lower blood pressure, especially in hypertensive subjects based on multiple clinical trials.
Shows anticancer effects against many types of cancer cells according to in vitro studies.
Prevents UV damage, photoaging and wrinkling when applied topically according to dermatological studies.
Improves immune response after prolonged exercise stress in active male adults.
May reduce risk of upper respiratory infections like the common cold in marathon athletes.
Overall, quercetin exhibits benefits as both an oral supplement and ingredient in skin care products.
Taking Quercetin and Coenzyme Q10 Together
Since quercetin and CoQ10 work via different mechanisms, they can have synergistic and complementary effects when taken together. Potential benefits of stacking quercetin and CoQ10 include:
Greater antioxidant protection through regenerating each other’s antioxidant capacities.
Enhanced mitochondrial function and energy production.
Increased stamina and athletic performance.
Improved cardiovascular health markers.
Added protection for neurons and brain function.
Accelerated recovery from exercise.
Higher immunity against viral infections like the flu.
Augmented benefits for skin health and anti-aging.
Quercetin and CoQ10 supplements are safe to take together for most people at moderate dosages of up to 500 mg quercetin and 300 mg CoQ10 daily. Start slow at lower doses and watch for any potential side effects. Consult a doctor before combining if you have any medical conditions or take prescription medications.
Which is Better: Quercetin or CoQ10?
Whether quercetin or CoQ10 is “better” depends on your specific health goals and needs:
For allergies, respiratory benefits, and cardiovascular health: quercetin may have more targeted effects.
For energy, skin health, fertility, and cognitive function: CoQ10 may be superior.
For athletic performance, quicker exercise recovery, and muscle gain: quercetin appears more promising from available research.
For mitochondrial support, antioxidant capacity, and anti-aging: CoQ10 is more directly involved.
For inflammatory conditions like arthritis or IBS: quercetin has more evidence.
For budget-friendly antioxidant support: quercetin is lower cost (Buy Bulk Quercetin).
In many cases, combining quercetin and CoQ10 together provides the most enhanced benefits. But assess your personal health goals and needs, then select the antioxidant(s) that can best target and support those specific areas.
Conclusion
Quercetin and CoQ10 are both incredibly beneficial daily antioxidants that promote health through different mechanisms. Quercetin directly scavenges free radicals while CoQ10 regenerates other antioxidants and fuels mitochondrial energy production. Their combined effects can enhance exercise performance, cardiovascular health, immunity, anti-aging, and more. Choose quercetin or CoQ10 alone depending on your specific health goals or take both together for amplified antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. Further research should continue to uncover optimized usage and dosing strategies.
FAQs about Quercetin and CoQ10
What foods contain quercetin and CoQ10?
Quercetin is highest in fruits and vegetables like apples, onions, tea, broccoli, berries, and capers. Good CoQ10 food sources include meat, fish, nuts, oils and whole grains.
What are the side effects of quercetin and CoQ10?
At typical doses, both are generally well tolerated. High doses may cause digestive upset like nausea or headaches. Quercetin can interact with some medications like blood thinners.
Can I take quercetin and CoQ10 at the same time?
Yes, quercetin and CoQ10 are safe to take together and may offer synergistic effects. Start with lower doses of each and increase gradually.
When should I take quercetin and CoQ10 each day?
The best time to take quercetin is in the morning with or after a meal. CoQ10 is best absorbed with food containing fat. Take CoQ10 with breakfast or lunch.
Are quercetin and CoQ10 vegan/vegetarian friendly?
Yes, supplements of both quercetin and CoQ10 suitable for vegan/vegetarian diets are widely available. CoQ10 can be synthetically produced.
Do quercetin and CoQ10 interact with any medications?
Quercetin may interact with blood thinners. CoQ10 may lower blood pressure, so monitor closely if on antihypertensive meds. Check with a doctor about any interactions.
How long until I notice the effects of quercetin and CoQ10?
Consistent daily use for 2-4 weeks is typically required to notice results of quercetin or CoQ10 supplementation. Effects become more pronounced with sustained use.
Is it safe to take quercetin and CoQ10 long term?
Yes, existing research has not found any negative effects of long term usage at moderate dosages for either quercetin or CoQ10. They appear safe for regular, sustained daily use.
Are quercetin and CoQ10 recommended for children?
Quercetin and CoQ10 supplements are not recommended for children without medical guidance. Consult a pediatrician before use in minors.
References
Boots, A. W., Haenen, G. R., & Bast, A. (2008). Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical. European journal of pharmacology, 585(2-3), 325–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.03.008
D'Andrea, G. (2015). Quercetin: A flavonol with multifaceted therapeutic applications?. Fitoterapia, 106, 256–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.09.018
About Author

Celine Xu is a botanist with over 15 years of experience researching and developing plant extracts for nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. She leads an R&D team focused on identification, cultivation and extraction of medicinal plants. Celine Xu earned a Ph.D. in Plant Biology has authored numerous articles in peer-reviewed journals about the health benefits of specific phytochemicals. She frequently speaks at industry conferences about new developments in plant extract research. Celine Xu is dedicated to advancing the scientific understanding of how targeted plant compounds can be used to improve human health.
Related Industry Knowledge
- what is Alfalfa Extract Powder
- Does berberine reduce belly fat?
- Is it good to take Vitamin E Everyday?
- What flavor is nutmeg powder?
- When to Take Berberine for Weight Loss
- How long does curcumin take to work
- What Foods Contain Capsaicin?
- D-Serine vs L-Serine
- OPC Grape Extract Powder: A Comprehensive Guide
- Gynostemma Pentaphyllum Saponin: Exploring the Health Benefits of this Powerful Herbal Extract








