L-serine VS Phosphatidylserine
L-serine and phosphatidylserine are two famous enhancements utilized for mind wellbeing. While they share a few primary similitudes and advantages, significant contrasts exist too. I'll compare and contrast L-serine and phosphatidylserine, examining their mechanisms, applications, safety profiles, and cognitive enhancement efficacy.
What is L-serine?
L serine powder bulk is one of the normally happening proteinogenic amino acids integrated into proteins during interpretation. Since the body can make it on its own but may need to get it from other sources, it is considered to be conditionally essential. L-serine upholds protein combination, cell flagging, digestion, insusceptible capability and appropriate neurotransmission. The brain and central nervous system are where it is most concentrated.
What is Phosphatidylserine?
A phospholipid compound made of serine and other molecules is called phosphatidylserine. It is a critical part of cell layers, particularly in the cerebrum. Most phosphatidylserine is created from soy or sunflower lecithin. It is involved in cell signaling pathways and contributes to the fluidity of the membrane.

Difference Between L-serine and Phosphatidylserine
Regardless of some cross-over, key contrasts between L-serine and phosphatidylserine include:
Structure - L-serine is a solitary amino corrosive while phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid compound.
Amalgamation - L-serine can be straightforwardly integrated by the body yet phosphatidylserine should be gathered from phospholipid forerunners.
Components - L-serine is associated with protein blend. Phosphatidylserine manages cell film capability.
Concentration: The body produces L-serine everywhere. The brain is where phosphatidylserine is concentrated.
Source - L serine bulk is gotten from high protein food sources. Phosphatidylserine supplements are gotten from soy or sunflowers.
The recommended daily dose of L-serine is 500-1500 milligrams. 100-400 milligrams of phosphatidylserine are common.
So in synopsis, L-serine is an amino corrosive forerunner while phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid finished result that consolidates serine.
What are the Similarities Between L-serine and Phosphatidylserine?
L-serine and phosphatidylserine share a few similarities despite their differences, such as:
Benefits to brain health: Both enhance cognition, focus, memory, and mood.
Nerve support - Assist with keeping up with appropriate nerve drive transmission.
Maintain fluidity and membrane signaling by maintaining cell membrane integrity.
Neuroprotective impacts - Safeguard neurons and synaptic associations from harm.
Effects on aging: Prevent cognitive decline caused by aging.
Security - All around endured with negligible aftereffects at standard portions.
So while their components vary, L-serine and phosphatidylserine supplements have corresponding advantages for cerebrum construction and capability.

Benefits of L-serine
Research demonstrates supplemental l serine powder might offer advantages including:
Further develops memory, learning and fixation
Increments synapses like glycine
Animates nerve development factor creation
Upholds insusceptible capability and digestion
Helps creation of glutathione cell reinforcement
Advances muscle development and exercise execution
Upgrades skin flexibility and hydration
Balances mind-set and oversees pressure
L serine bulk's most concentrated on impacts include streamlining intellectual ability, nerve wellbeing, invulnerability and digestion. The most effective doses appear to be between 500 and 1500 milligrams.
Benefits of Phosphatidylserine
According to studies, phosphatidylserine can:
Reduce the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's Lower cortisol levels induced by stress Aid symptoms of ADHD and depression Improve exercise performance and recovery Doses of 100-400mg appear to be most beneficial for phosphatidylserine’s brain-boosting activity, especially in the elderly. Improve cognitive function, especially in the elderly. Combat age-related memory loss and cognitive decline. Enhance neural connectivity and neuroplasticity. Support cell membrane integrity and fluidity.
Is phosphatidylserine same as L-serine?
L-serine is not the same as phosphatidylserine. L-serine is one of the amino acid parts bound to the phosphatidylserine particle. Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid comprised of serine, phosphate, and unsaturated fat gatherings. So while L-serine is held inside phosphatidylserine, they are particular mixtures.
Is L-serine good for the brain?
Indeed, l serine powder bulk seems valuable for cerebrum capability. L-serine helps with cognition, mood, memory, learning, concentration, and nerve transmission because it is a part of brain proteins and neurotransmitters. Taking L-serine supplements has been shown to improve verbal fluency, thinking skills, memory, and cognition scores.

What are the benefits of L-serine?
As well as improving mind execution, research shows L-serine may:
Help manage stress, anxiety, and depression Protect liver function Boost glutathione antioxidant activity Aid peripheral neuropathy Slow aging and extend lifespan L-serine is necessary for protein synthesis, nerve function, cell membrane stability, and proper neurotransmission. It also helps increase exercise endurance and muscle growth. Supplemental dosages from 500-1500mg everyday seem to upgrade generally wellbeing.
What is the difference between serine and phosphatidylcholine?
The primary distinctions among serine and phosphatidylcholine include:
Serine is an amino acid, while phosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid compound.
Serine contains only a focal carbon particle. Phosphatidylcholine contains glycerol, choline and phosphate gatherings.
Serine is integrated into proteins. One of the components of cell membranes is phosphatidylcholine.
Serine can be gotten from high protein food varieties. Phosphatidylcholine is procured from lecithin supplements.
Both give choline, however serve unmistakable jobs - serine for proteins and phosphatidylcholine for layers.
So in outline, serine is an amino corrosive forerunner, while phosphatidylcholine is a complicated phospholipid, however both proposition cerebrum benefits.
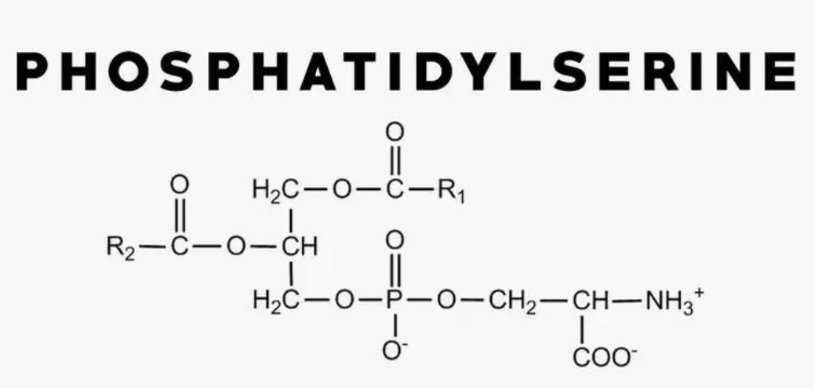
What's the difference between phosphorylated serine and phosphatidylserine?
Phosphorylated serine alludes to the amino corrosive serine with a phosphate bunch connected. Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid compound made out of serine and extra particles bound to a glycerol spine.
Principal contrasts include:
Phosphorylated serine is a changed solitary amino corrosive. Phosphatidylserine is an intricate phospholipid.
Enzymatic phosphorylation adds phosphorus to serine. Phosphatidylserine is gathered from serine, glycerol, unsaturated fats and different phospholipids.
Phosphorylated serine is a middle in metabolic pathways. Phosphatidylserine is a key useful finished result tracked down in films.
The regulation of proteins is influenced by phosphorylated serine. Signaling and membrane structure are affected by phosphatidylserine.
Therefore, phosphatidylserine incorporates serine residues into membrane phospholipids through more complex biosynthesis, whereas phosphorylated serine is the phosphate addition to serine alone.
What is phosphatidyl L-serine?
Phosphatidyl L-serine is a phospholipid compound that contains the amino corrosive L-serine bound to a glycerophosphate spine alongside unsaturated fats. In particular in the brain, it is an essential component of cell membranes.
Phosphatidyl L-serine is blended endogenously from different phospholipids or acquired from soy lecithin supplements. Nerve transmission, neurotransmitter release, membrane fluidity, and cell signaling are all regulated by it.
Cognitive function, memory, learning, concentration, mood, exercise performance, and slowing down age-related neurodegeneration may all reap the benefits of phosphatidyl L-serine, according to research. It appears that 100-500mg doses are effective.

What is the function of L-serine?
A few critical elements of the amino corrosive L-serine include:
Protein combination - L-serine is integrated into proteins during interpretation to assemble appropriate design.
It is a precursor of the neurotransmitters glycine, D-serine, serotonin, and melatonin in the neurotransmission process.
Phospholipids like phosphatidylserine are necessary for the integrity of cell membranes.
Digestion - Vital for unsaturated fat amalgamation and digestion of fats/lipids.
Insusceptibility - Expected for ideal white platelet multiplication and immune response blend.
Nerve capability - Supports appropriate nerve drive conduction and correspondence.
Muscle function: It stimulates the growth of muscle tissue and the production of the necessary proteins for growth.
So in synopsis, L-serine assumes essential parts in protein creation, neurotransmission, cell films, digestion, resistance, nerve wellbeing and muscle capability. It is an essential, versatile amino acid for all body processes.
All in all, L-serine and phosphatidylserine are unmistakable mixtures offering comparative cerebrum benefits. Despite the differences in their mechanisms, both are necessary supplements for maintaining optimal brain structure and cognitive performance.
Summary – L-serine vs Phosphatidylserine
In summary, l serine powder bulk is an amino acid antecedent required for protein blend, while phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid finished result made mostly out of serine buildups. L-serine fills in as a structure block, while phosphatidylserine controls cell film properties fundamental for cerebrum capability. Both deal mental upgrade, making them well known nootropic supplements.
References
Dell, M. J., and Smith, K. (2015). The human brain and phosphatidylserine. Sustenance, 31(6), 781-786.
Richter, Y., Herzog, Y., Lifshitz, Y., Hayun, R., and Zchut, S. (2013). The impact of soybean-determined phosphatidylserine on mental execution in old with abstract memory protests: a pilot study. 8, 557, Clinical interventions in aging.
A. Kato-Kataoka, M. Sakai, R. Ebina, C. Nonaka, T. Asano, and T. Miyamori are among the authors. Soybean-determined phosphatidylserine further develops memory capability of the old Japanese subjects with memory objections. Diary of clinical organic chemistry and sustenance, 47(3), 246-255.
Hellhammer, J., Waladkhani, A. R., Legend, T., and Buss, C. (2010). The effects of milk phospholipid on healthy human subjects' memory functions. Research in nutrition, 30(10), 693-697.
Schauss, A. G., Stenehjem, J., Park, J., Endres, J. R., Clewell, A., Rainbow, J., and Peterson, C. T. (2012). Impact of the original dietary enhancement, EssentraTM, on mental execution in sound workers: a randomized, twofold visually impaired, fake treatment controlled study. Diary of the American School of Sustenance, 31(2), 147-154.
About Author

Celine Xu is a botanist with over 15 years of experience researching and developing plant extracts for nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. She leads an R&D team focused on identification, cultivation and extraction of medicinal plants. Celine Xu earned a Ph.D. in Plant Biology has authored numerous articles in peer-reviewed journals about the health benefits of specific phytochemicals. She frequently speaks at industry conferences about new developments in plant extract research. Celine Xu is dedicated to advancing the scientific understanding of how targeted plant compounds can be used to improve human health.
Related Industry Knowledge
- What are the functions of Melilotus Officinalis Extract?
- Can you dissolve acyclovir in water?
- What is Allantoin Powder?
- How do you take proline powder?
- Is L-arginine the same as L-ornithine?
- What is Apple Extract
- What happens if you take too much apigenin?
- Chicory Root vs Jerusalem Artichoke Inulin
- Can You Take Berberine and Inositol Together?
- Lentinan Extract: Unveiling the Power of Mushroom-Based Health







