Is inulin a prebiotic
We are each apprehensive of how vital a fiber-rich diet is for heart health, digestive health, bowel movements, and more. But did you know that specific types of filaments have benefits beyond what we generally suppose about fiber?
One, in particular, called inulin, is a type of fiber touted for its salutary part in gut and metabolic health, besides the typical places in digestive health.
Although there are several types of inulin, they all have one thing in common their capability to act like prebiotic fiber. noway heard of it?
Nope, it's not the conventional probiotics we hear about each over the health news. They are a salutary fiber that serves as food for the salutary bacteria in your gut. Because it can not be broken down or absorbed in the GI tract, it offers body-wide benefits.
The same goes for inulin — because humans do not retain the enzymes demanded to break it down, it passes through the digestive tract complete and feeds the good gut bugs( these guys are the probiotics) while offering other benefits similar as lowering cholesterol and promoting malnutrition. Sounds like a real winner, right?
So, if you are strange with inulin, you are in the right place. This composition explains what you need to know about the prebiotic fiber inulin and how it supports gut health( and overall full- body health).
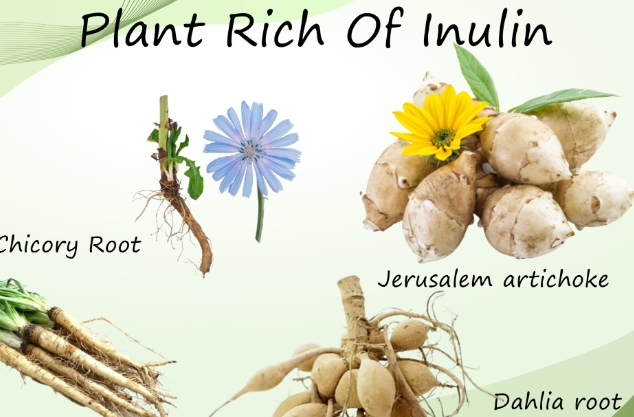
What Is Inulin?
At first regard, you may suppose we are talking about insulin, but we are not. Inulin is a answerable factory fiber set up in high quantities in thousands of factory species, especially chicory root.
You will also find it in effects like bananas, onions, garlic, asparagus, and Jerusalem artichokes all foods we call prebiotic foods.
As a prebiotic fiber, humans do not retain the enzymes necessary to break it down, so it travels through the digestive system fairly untouched.
While you may suppose," what's the point of eating commodity that is not going to be absorbed?" we get it but there are plenitude of benefits.
Salutary filaments like bulk inulin have been consumed for hundreds of times to ameliorate bowel chronicity, digestive health, and heart health. And stylish of all, it's fully natural!
On a specialized position, inulin is a type of fructan, oligofructose carbohydrate 1. It's naturally present in factory roots and stems as a source of energy.
And although you may not suppose about fiber as a source of sugar, it is and it contains about 75 smaller calories than white sugar per gram and has minimum effect on blood glucose, making it a good option for people with diabetes and those with glucose imbalances. Because of its osmotically active parcels, it resists breakdown by digestive enzymes.
Of the bacterial species that use prebiotics, inulin- type fructans have a specific colonic turmoil directed toward bifidobacteria, which can break down and use inulin- type fructans as a result of enjoying the fructofuranosidase enzyme 2. So, they've a competitive advantage in a mixed species terrain similar as the gut.
But what is so good about inulin? Studies show that inulin is essential for mortal health because of its" prebiotic effect," meaning it allows the healthy bacterial species( probiotics) that make up the gut( microbiome) to thrive and gain 3. But it also binds to cholesterol, which can reduce situations and the associated threat of metabolic pattern.
What is The Difference Between Inulin And Psyllium?
piecemeal from inulin, there is another answerable fiber we generally hear about, psyllium cocoon. As the name suggests, psyllium cocoon is uprooted from the cocoons of the Plantago ovata factory's seeds.
For anyone looking to ameliorate digestion and cholesterol situations, it's considered gold 4. It's the backbone of utmost fiber supplements and numerous high- fiber snacks.
Compared to inulin and other fiber supplements, psyllium absorbs further water. It's lower fermentable in the gut, which means it expands and becomes sticky when consumed, helping keep bowel movements regular, precluding constipation, and perfecting diarrhea.
Because inulin does not absorb water to the same capacity, it does not have the same laxative effect.

Inulin And Health The 5 Benefits You Need To Know About
1. Relieves and reduces constipation
Backed up? Although there are several causes of constipation, not consuming enough salutary fiber is a big one — and inulin is excellent for supporting that.
Get on board.
subscribe up for emails to get further information.
Dispatch address
Enter your dispatch
SUBSCRIBE
Because of its chemical composition, wholesale inulin forms a gel- suchlike substance that's great for getting the intestine moving. When it forms a gel, it has a structure analogous to fats that slick the GI tract and reduce the threat of effects like hemorrhoids.
On top of bulking up droppings and adding fecal biomass and water content, it also helps to ameliorate bowel movement frequence because it fleetly ferments in the colon to feed the salutary bacteria 5, 6.
A 2017 study published in the International Journal of Food lores and Nutrition set up that supplementation with 4g of Orafti ® Inulin three times daily in chronically constipated grown-ups significantly bettered bowel function compared to placebo 7.
2. Supports salutary bacteria in the gut
Because inulin is anon-digestible prebiotic fiber, it passes through the GI tract fairly complete and unabsorbed. As it passes, it naturally starts to raise, furnishing food for the salutary bacterial species that colonize the gut, especially Bifidobacterium.
Studies show that oligofructose acts like a prebiotic to enhance the filling of the gut and colon, alter the biodiversity of the gut, and modulate the endocrine and vulnerable functions 8.
Because it promotes the growth and proliferation of healthy bacteria, it may also reduce the presence of potentially dangerous bones that beget inflammation.
3. Reduces appetite
still, adding some prebiotic fiber to your diet may help, thanks to its low- calorie content and absorbability, If you struggle with weight loss.
When bulk inulin powder combines with water, it provides bulk and creates a gel- suchlike substance that expands and increases the size of the contents in the digestive tract. As similar, it can reduce appetite and jones , making it a solid option for weight loss.
Prebiotic filaments also help delay gastric evacuating and take up more space in the stomach, thereby promoting malnutrition and helping reduce energy input 9.
4. Improves heart health and reduces metabolic pattern threat factors
There are ample ways to ameliorate heart health naturally, but did you know fiber can do so, too? When inulin passes through the Gi tract, it picks up poisons, tastes, fat, and cholesterol, helping with their excretion this is why high- fiber diets are frequently linked to bettered cardiovascular issues 10.
Studies find that boosting your fiber input can help reduce blood cholesterol situations, reduce arteriosclerosis threat, and maintain healthy glucose situations 11.
How is this possible? There is an inverse relationship between salutary fiber content and systolic and diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol situations, and triglycerides. Simply put, answerable fiber helps reduce LDL cholesterol b blocking its immersion.
Inulin also will not increase your blood glucose situations! Since it's not metabolized in the body, it does not spark insulin release and a shaft in blood sugar 12.
5. Enhances calcium immersion
Although not directly related to gut health, calcium is essential for numerous physiological functions in the body, including bone and muscle health. Some exploration shows that hitting your fiber input could ameliorate the immersion of specific minerals, similar as calcium and magnesium 13. How does fiber support nutrient immersion? You can thank its prebiotic effect on the gut.
A 2005 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition looked at the goods of inulin- type fructans supplementation on calcium immersion and bone mineral accretion in pubertal adolescents 13.
They set up that diurnal supplementation with prebiotic short- and long- chain organic inulin powder bulk- type fructans redounded in significant increases in calcium immersion and lesser bone mineralization during ages of pubertal growth.
As similar, in populations susceptible to calcium insufficiency — youthful ladies andpost-menopausal women — inulin supplementation may be salutary for enhancing calcium immersion and supporting bone health.
Takeaway communication Grounded on what we just talked about, the benefits of answerable fiber extend far beyond just the gut. Then is a list of the benefits of inulin- type prebiotics
Improves gastrointestinal and gut health
May help certain habitual conditions
Improves blood sugar control and protects against type 2 diabetes
Supports growth and development in kiddies
Improves cholesterol situations and lipid metabolism
Improves bone mineralization
May reduce the threat of rotundity
Enhances impunity

Where To Find Inulin
Although bulk organic inulin powder is fluently set up in supplemental form, it's also extensively available in numerous factory foods they're what we call prebiotic foods! Try adding some of these to your diet to boost your inulin input
Chicory root fiber
Asparagus
Leeks
Onions
Bananas
Plantains
Picked wheat
Garlic
Fresh sauces
Yams
Jerusalem artichokes
Burdock root
Echinacea
Jicama
Yacon root
Salutary filaments are the primary food source for the good bugs in your gut, which is why we promote a diet rich in fruits, lush green vegetables, sap, and legumes.
But if you are looking to increase your input further, consider commodity like Performance Lab Prebiotic — it's a 2- in- 1 answerable fiber and prebiotic supplement designed for full- diapason microbiome support.
Unlike conventional probiotics that introduce new colonies into the gut, Prebiotic nourishes those that formerly live for digestive comfort and peace of mind.
How important Inulin Do You Need?
There is no definitive quantum of inulin to support gut health, but it can be consumed as part of your diurnal fiber input. Grounded on archaeological substantiation, ancient populations thriving on a primarily factory- grounded diet consumed around 135 grams of prebiotic inulin- type fructans daily 14.
Although it's hard to estimate exactly how important the average adult consumes — it varies vastly grounded on diet — utmost Americans consume far lower than the recommended diurnal fiber input, around 10- 15 grams, from fruits, vegetables, and reused foods with added chicory root 15.
On normal, grown-ups should consume 20- 35 grams of fiber daily from whole food sources. But because inulin is fluently added to foods like oatmeal, authorities, and ignited goods without impacting their taste, it's easy to increase your input!
Generally speaking, start with 3- 5 grams of inulin per day and work your way up to a diurnal cure between 5 and 15 grams for optimal benefits.
Inulin is considered one of the best- studied prebiotic filaments and offers unique benefits for gut health. But what exactly are prebiotics, and why is inulin an ideal choice? This composition will examine the substantiation on inulin as a prebiotic.
Is inulin a good prebiotic?
Prebiotics are specialized factory filaments that pass undigested through the small intestine and widely stimulate the growth of salutary bacteria in the colon. The inedible nature of prebiotics allows them to serve as" food" for probiotics.
exploration shows inulin fits the criteria for an effective prebiotic
picky bifidogenic effect Multiple studies demonstrate inulin significantly increases bifidobacteria counts, one of the most salutary groups of gut bacteria( 1).
Resistant to gastric acidity Inulin withstands low pH and digestive enzymes to reach the colon complete( 2).
instigated by gut foliage Colonic bacteria like Bifidobacterium retain enzymes to break down and use inulin( 3).
Modulates impunity and pathogens Inulin improves gut hedge function, reduces inflammation, and inhibits pathogens likeC. difficile( 4).
safe-deposit box for mortal consumption Inulin is Generally honored as safe-deposit box( GRAS) and well- permitted in boluses up to 30 grams per day( 5).
For these reasons, inulin is considered one of the most considerably delved and effective prebiotic filaments presently available. It has a robust substantiation base supporting its prebiotic exertion.
What type of prebiotic is inulin?
Inulin belongs to a class of prebiotics known as fructans, which are carbohydrates conforming of chains of fructose motes.
Botanically, inulin is a polysaccharide of fructose produced by numerous shops as an energy reserve. Chicory root contains the loftiest attention, around 15- 20 by weight( 6).
Structurally, inulin contains beta- 2,1 linked fructose chains with a glucose starter unit. The degree of polymerization ranges from 2 to 70 fructose units( 7).
Longer chain inulins are more answerable and have lesser prebiotic goods compared to shorter oligofructose motes. Inulin is also distinct from other prebiotics like galactooligosaccharides( GOS).
So in summary, inulin is a well- defined fructan prebiotic with a unique chemical structure that confers significant gut health benefits.
Is prebiotic fiber the same as inulin?
While inulin is a prebiotic fiber, not all prebiotic filaments are inulin. The term “ prebiotic fiber ” refers to inedible factory filaments that promote growth of salutary gut bacteria. This includes
Inulin – Fructan fiber from chicory, onions, asparagus,etc.
Galacto- oligosaccharides( GOS) – From lactose digestion or soybeans.
Resistant bounce – bounce that resists digestion, set up in grains, potatoes,etc.
Arabinoxylan – Hemicellulose fiber set up in wheat, psyllium,etc.
Pectin – Answerable fiber from fruits and vegetables.
Each prebiotic fiber has unique parcels, but all meet the description of widely stimulating target gut bacteria. Inulin is one of the most common supplements due to its bifidogenic goods.
While foods like onions contain some inulin, supplements offer advanced chastity and prebiotic tablets. Both insulated and food- grounded prebiotics can support microbiome health. But inulin itself is just one type among numerous prebiotic filaments.
References
[1] Kolida, S., Meyer, D., & Gibson, G. R. (2007). A double-blind placebo-controlled study to establish the bifidogenic dose of inulin in healthy humans. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 61(10), 1189–1195.
[2] Bonnand-Ducasse, M., Della Valle, G., Lefranc-Millot, C., & Guérin-Deremaux, L. (2015). Effect of inulin on bread preservation, textural and sensory properties during storage. Food Chemistry, 197, 302–310.
[3] Scott, K. P., Martin, J. C., Duncan, S. H., & Flint, H. J. (2014). Prebiotic stimulation of human colonic butyrate-producing bacteria and bifidobacteria, in vitro. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 87(1), 30–40.
[4] Childs, C. E., Roytio, H., Alhoniemi, E., Fekete, A. A., Forssten, S. D., Hudjec, N., Lim, Y. N., Steger, C. J., Yaqoob, P., Tuohy, K. M., Rastall, R. A., Ouwehand, A. C., & Gibson, G. R. (2014). Xylo-oligosaccharides alone or in synbiotic combination with Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis induce bifidogenesis and modulate markers of immune function in healthy adults: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, factorial cross-over study. The British Journal Of Nutrition, 111(11), 1945–1956.
[5] EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies. (2015). Scientific opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to “native chicory inulin” and maintenance of normal defecation by increasing stool frequency pursuant to Article 13.5 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/20061. EFSA Journal, 13(1).
[6] Franck, A. (2002). Technological functionality of inulin and oligofructose. British Journal of Nutrition, 87(S2), S287-S291.
[7] Niness, K. R. (1999). Inulin and oligofructose: what are they?. The Journal of nutrition, 129(7), 1402S-1406S.
ABOUT AUTHOR

Celine Xu is a botanist with over 15 years of experience researching and developing plant extracts for nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. She leads an R&D team focused on identification, cultivation and extraction of medicinal plants. Celine Xu earned a Ph.D. in Plant Biology from UC Berkeley and has authored numerous articles in peer-reviewed journals about the health benefits of specific phytochemicals. She frequently speaks at industry conferences about new developments in plant extract research. Celine Xu is dedicated to advancing the scientific understanding of how targeted plant compounds can be used to improve human health.
Related Industry Knowledge
- What are the functions of Melilotus Officinalis Extract?
- Can you dissolve acyclovir in water?
- Does Stevia Taste Like Sugar
- Is Vitamin E Powder good for your skin?
- Is berberine like Ozempic?
- Inulin Weight Loss
- How to Eat Persimmons
- Unveiling the Wonders of Ganoderma Lucidum Extract Powder
- The Power of Pumpkin Protein: A Nutritional Powerhouse for Your Health
- The Power of Rhamnus Frangula Powder: Enhancing Digestion and Wellness Naturally







